RIGHT INFORMATION ABOUT HEALTHY FOOD
Eating Healthy Food is essential for sustenance, providing us with energy, nutrients, and pleasure. It encompasses a wide range of flavors, textures, and cultural traditions, reflecting the diversity of our world. A balanced diet includes carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals, promoting overall health. However, food choices vary widely, influenced by personal preferences, dietary restrictions, and cultural backgrounds. The global food industry is vast, with agriculture, processing, and distribution playing critical roles. Unfortunately, issues such as food insecurity, food waste, and unsustainable practices persist, necessitating a shift towards more responsible and equitable food systems. Ultimately, food not only nourishes our bodies but also connects us to our heritage and the planet's future.
Indian food offers diverse flavors, rich in spices, and incorporates nutritious ingredients like lentils, vegetables, and whole grains, contributing to a balanced diet with potential health benefits.
Nutrient-rich diets support overall health, energy, and well-being.
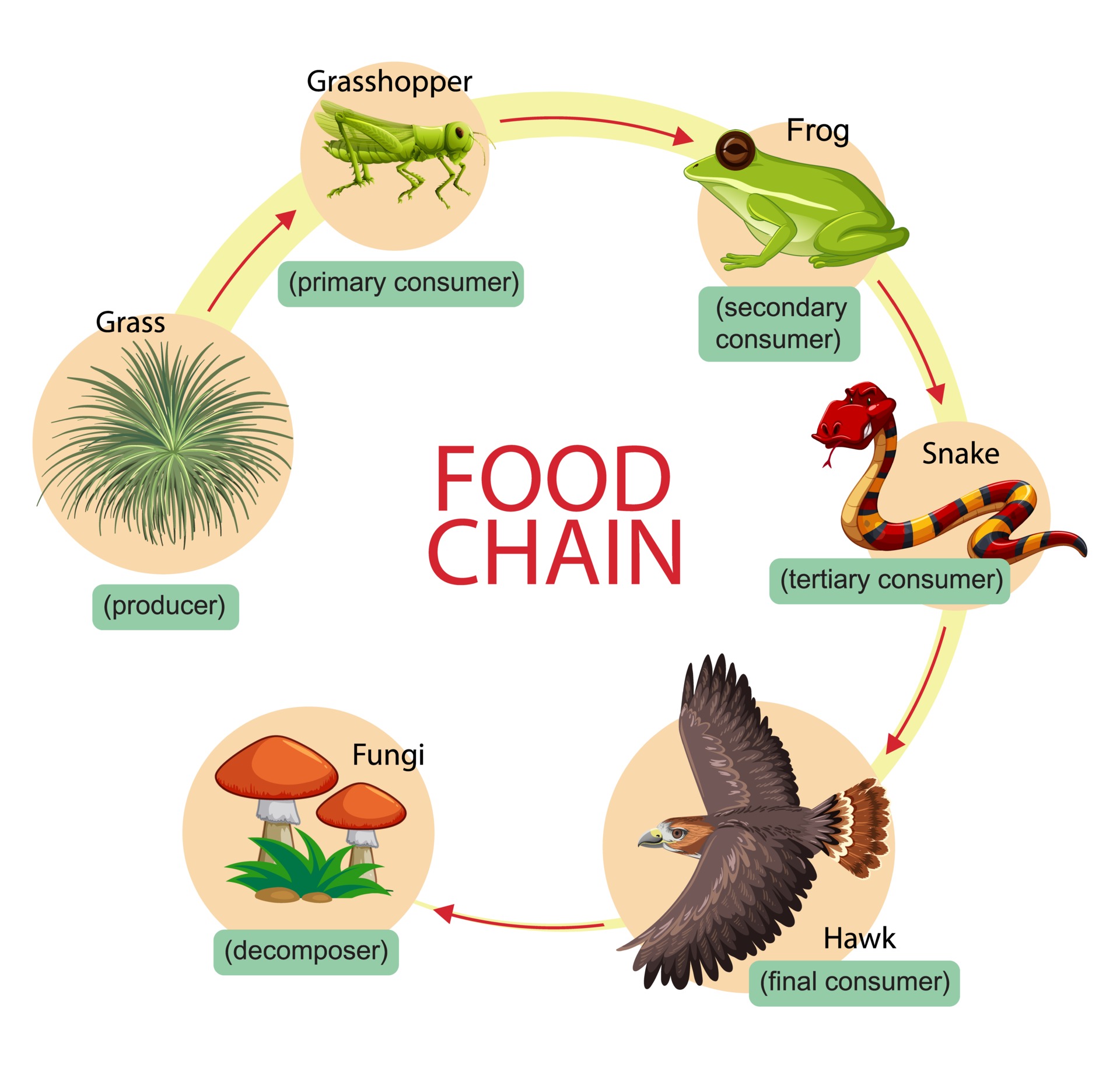
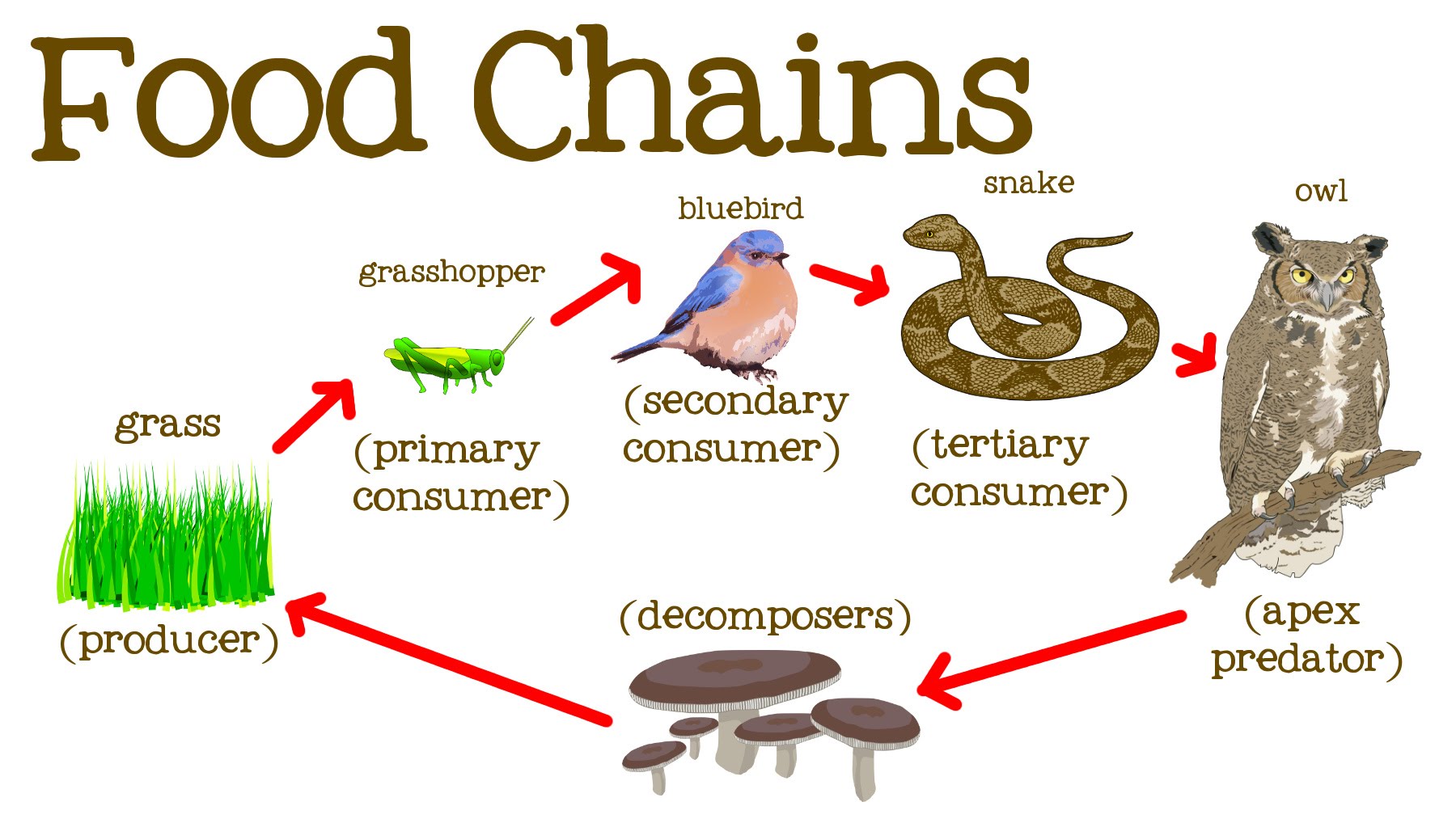
A food chain is a simplified model used in ecology to illustrate the transfer of energy and nutrients through a sequence of organisms in an ecosystem. It shows how energy and nutrients flow from one organism to another as they are consumed in a linear fashion. Typically, a food chain consists of several components:
- Producers: At the base of every food chain are the producers, which are usually plants or photosynthetic organisms like algae. Producers are capable of converting sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into energy-rich organic compounds through photosynthesis. These compounds, primarily in the form of carbohydrates, serve as the foundation of the food chain.
- Primary Consumers (Herbivores): The next level in the food chain consists of herbivores, which are organisms that feed directly on producers. They consume plants or algae to obtain energy and nutrients.
- Secondary Consumers (Carnivores): Above the herbivores are secondary consumers, which are carnivores. These animals prey on herbivores, consuming them for energy. They are often referred to as predators.
- Tertiary Consumers (Top Predators): In some food chains, there may be tertiary consumers, which are carnivores that feed on other carnivores. They occupy the top of the food chain.
- Decomposers: In addition to the primary chain, there are decomposers such as bacteria and fungi. These organisms break down the remains of dead plants and animals as well as other organic matter. They play a crucial role in recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
A classic example of a food chain is as follows:
Grass (Producer) -> Grasshopper (Primary Consumer) -> Frog (Secondary Consumer) -> Snake (Tertiary Consumer)
In reality, ecosystems are much more complex than simple linear food chains. They are often interconnected, forming intricate food webs. Organisms can have multiple food sources, and energy and nutrients flow in multiple directions within an ecosystem. Additionally, some organisms may play roles as both consumers and decomposers at different stages of their life cycle.
Food chains and webs are essential for understanding how energy and nutrients move through ecosystems, regulate populations, and maintain ecological balance. Disruptions in these chains or webs can have far-reaching impacts on an ecosystem’s health and stability. Read More